Do you know, that… ?
Three weeks ago I wrote about creating a thread display configuration.
Now let's make a comparison, how the thread type affects the file size and rebuild time. Both parameters have a key impact on the performance of assemblies with a large number of fasteners.
- Cosmetic Threads. Fastest rebuild time and smallest file size.
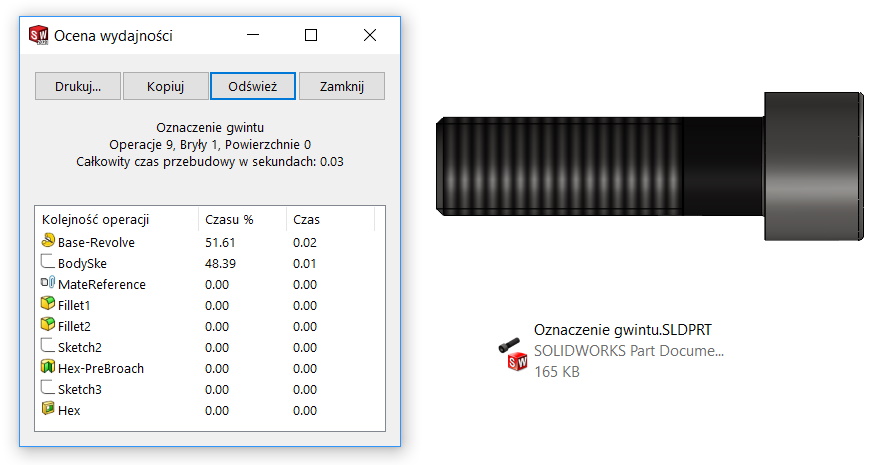
2. File with thread contour cut by revolving and duplicated with the pattern. Slightly larger size and longer reconstruction time.
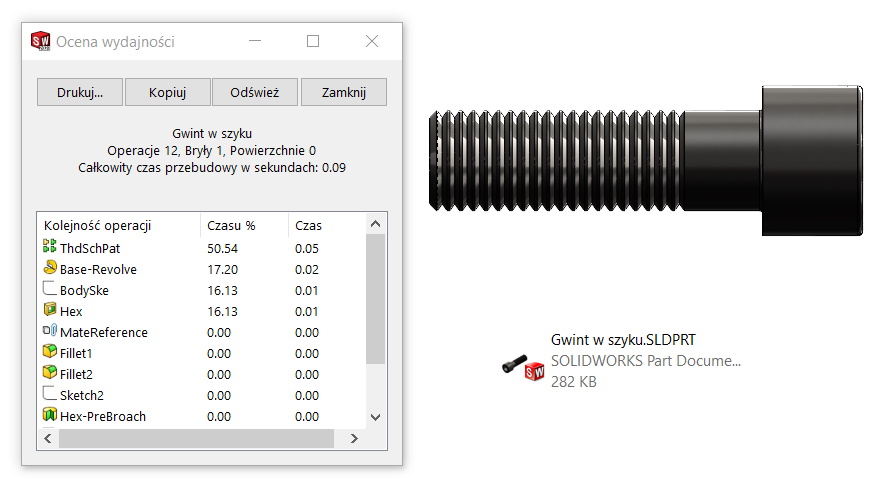
3. A file with a thread cut after a helix. Largest file size and longest rebuild time.
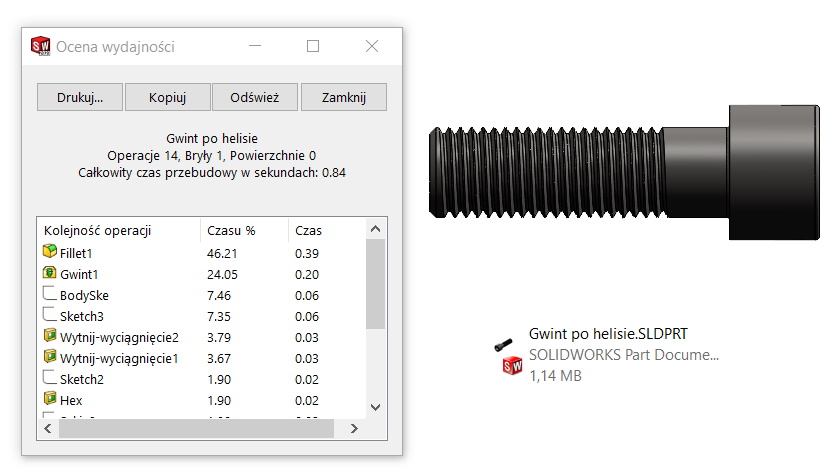
summarizing.
The most efficient solution is to apply Cosmetic Threads. This operation does not affect the file size and the rebuild time. In addition, it is an ideal solution to show in technical documentation. On the other hand, the worst choice is to make the thread in the form of a real helix profile. Independently, will you do it with an operation Thread or manually cut along the path (sweep feature), which is the helix – the result is the worst. The file size increases by an order of magnitude.
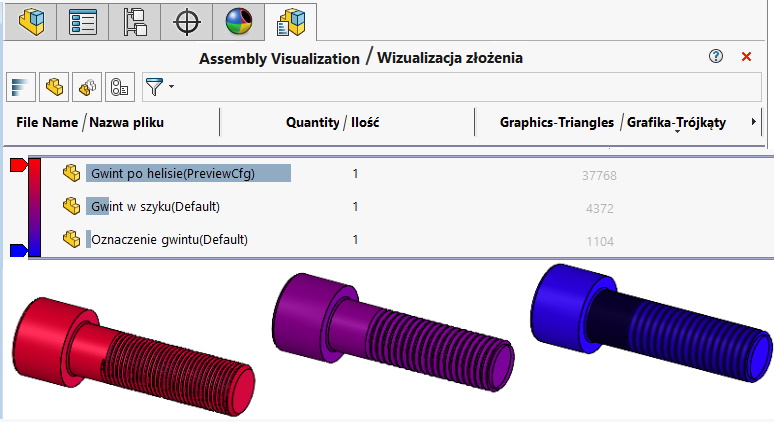
The use of a helix thread is justified only in the design of PET bottles, where the thread must be represented in the injection molding. The second example are 3D prints, where the thread profile is needed right away in the model. The third example are visualizations and assembly instructions, where you need to show the realistic appearance of the bolt / nut.
Leave a Reply